現象
ほぼタイトルで言い切っているけど。spring-batchでメタデータ保存でDBを使わなないようインメモリに格納するMapJobRepositoryFactoryBeanを使う場合が稀に良くある。この状況下で大量のstepを含むjobを実行すると徐々に実行速度が低下していく、という現象に遭遇した。
再現
大量のstepを手軽に再現するため、以下のように無限ループでstepを実行し続ける。つまりJobExecutionDeciderが常に同一値を返し、同一のstepに遷移する。こんな感じ。
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>11</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
package kagamihoge.springbatchslowdown; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecution; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.StepExecution; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.BatchConfigurationException; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.DefaultBatchConfigurer; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.EnableBatchProcessing; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.explore.JobExplorer; import org.springframework.batch.core.explore.support.MapJobExplorerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.FlowExecutionStatus; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.JobExecutionDecider; import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher; import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.RunIdIncrementer; import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher; import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.JobRepository; import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @EnableBatchProcessing public class BatchConfiguration { @Bean public Job job(JobBuilderFactory jobs, @Qualifier("s1") Step s1, JobExecutionDecider decider) { return jobs .get("myJob") .incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer()) .start(s1) .next(decider) .on("CONTINUE").to(s1) .end() .build(); } @Bean(name = "s1") public Step step1(StepBuilderFactory steps) { return steps.get("step1").tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } @Bean public JobExecutionDecider decider() { return new JobExecutionDecider() { @Override public FlowExecutionStatus decide(JobExecution jobExecution, StepExecution stepExecution) { return new FlowExecutionStatus("CONTINUE"); } }; } @Bean DefaultBatchConfigurer batchConfigurer() { return new DefaultBatchConfigurer() { private final JobRepository jobRepository; private final JobExplorer jobExplorer; private final JobLauncher jobLauncher; { MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean jobRepositoryFactory = new MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean(); try { this.jobRepository = jobRepositoryFactory.getObject(); MapJobExplorerFactoryBean jobExplorerFactory = new MapJobExplorerFactoryBean(jobRepositoryFactory); this.jobExplorer = jobExplorerFactory.getObject(); SimpleJobLauncher jobLauncher = new SimpleJobLauncher(); jobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository); jobLauncher.afterPropertiesSet(); this.jobLauncher = jobLauncher; } catch (Exception e) { throw new BatchConfigurationException(e); } } @Override public JobRepository getJobRepository() { return jobRepository; } @Override public JobExplorer getJobExplorer() { return jobExplorer; } @Override public JobLauncher getJobLauncher() { return jobLauncher; } }; } }
実行時の様子
以下にjvisualvmのキャプチャを示す。
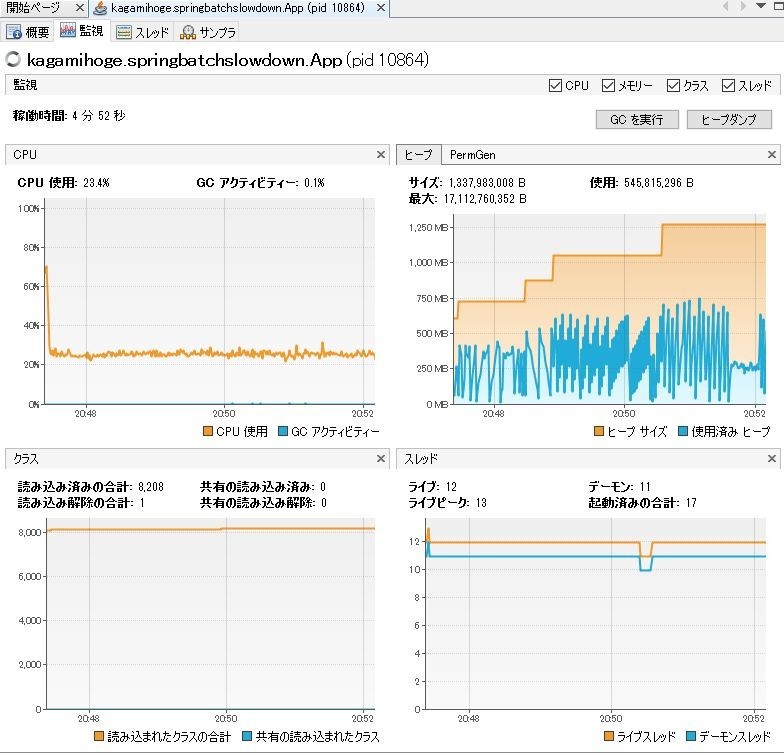
上記はだいたい5分くらい実行したところだが、ヒープサイズがどんどん膨らんでいく。使用済みヒープも徐々に増えてはいるようだが、どうも急激に増えて減ってを繰り返している、ように見える。
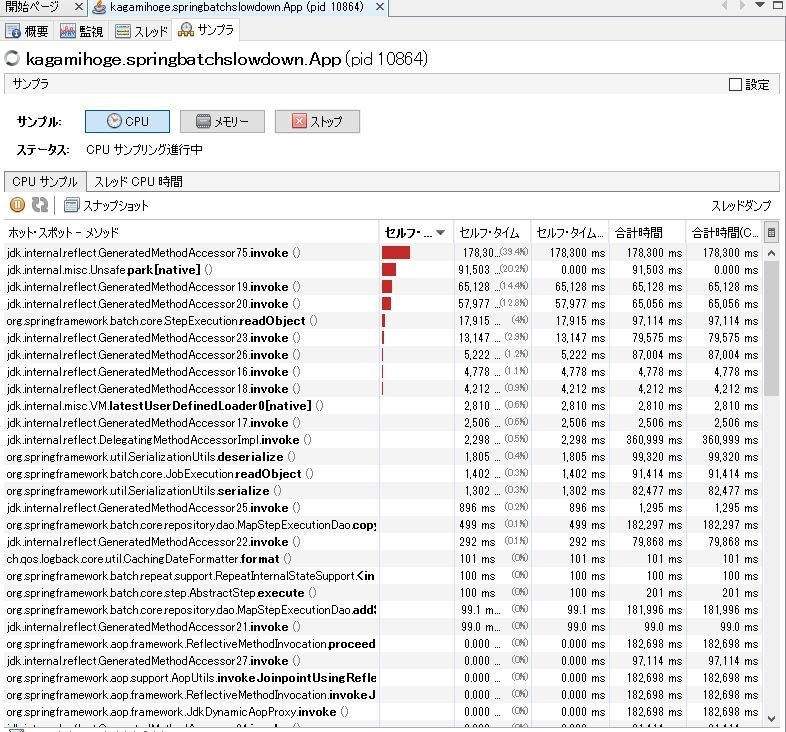
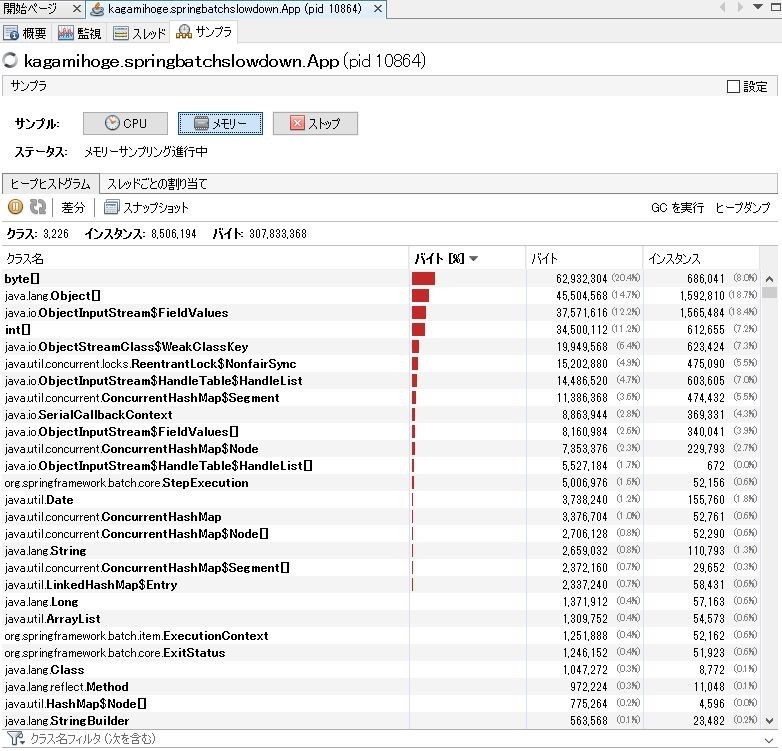
サンプラを見るとbyte[]が多数を占め、CPUを見るとリフレクションが実行時間のうち大半を占めている。
怪しそうなのは、上位にあるStepExecutionObjectとかConcurrentHashMapとか、シリアライズ関連のObjectInputStreamとからへん。なので原因調べるときはその辺から調べていった。
原因
概要
MapJobRepositoryFactoryBeanはjob-executionの格納にMapJobExecutionDaoを使用する。これは内部的にはConcurrentHashMap<Long, JobExecution>()で保存し、また、job-executionに関連付くstep-executionのコレクションを保持している。次に、そのマップ保存時にオリジナルのJobExecutionをコピーするが、その実装がシリアライズandデシリアライズになっている。
詳細
MapJobExecutionDaoは以下のようなプロパティがあり、ここでjobExecution idとJobExecutionのマップを持っている。また、JobExecutionはstep-executionを保持するstepExecutionsのコレクションがある。
public class MapJobExecutionDao implements JobExecutionDao { private final ConcurrentMap<Long, JobExecution> executionsById = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, JobExecution>();
@SuppressWarnings("serial") public class JobExecution extends Entity { .... private volatile Collection<StepExecution> stepExecutions = Collections.synchronizedSet(new LinkedHashSet<>());
step実行時は以下のMapStepExecutionDaoがstep-executionの追加処理を行う。以下のように、job-exectuion -> step-executionのコレクションに追加する。なのでstepを大量に実行すれば無限にstep-executionが追加されていく。
public class MapStepExecutionDao implements StepExecutionDao { ... @Override public void updateStepExecution(StepExecution stepExecution) { Map<Long, StepExecution> executions = executionsByJobExecutionId.get(stepExecution.getJobExecutionId()); .... executions.put(stepExecution.getId(), copy);
ヒープサイズが拡大する点についてはこれで一応説明がつく。
次に、スローダウンの原因について。
MapJobExecutionDaoに話は戻るが、マップ保存の際にJobExecutionインスタンスをコピーする。で、コピーは以下のようにシリアライズ -> デシリアライズで実装している。
private static JobExecution copy(JobExecution original) { JobExecution copy = (JobExecution) SerializationUtils.deserialize(SerializationUtils.serialize(original)); return copy; }
前述のようにstep-executionコレクションはどんどんデカくなっていくので、当然、そのマップをシリアライズ -> デシリアライズする処理もどんどん遅くなっていく。この挙動は徐々にスローダウンする事象と一致する。クッソでかいコレクションをシリアライズ -> デシリアライズするのでゴミもクッソでかくなる。使用済みヒープが急激に増えては減ってはを繰り返すのはこの辺にある、と推測される。
対策
インメモリDBにメタデータを保存させる。
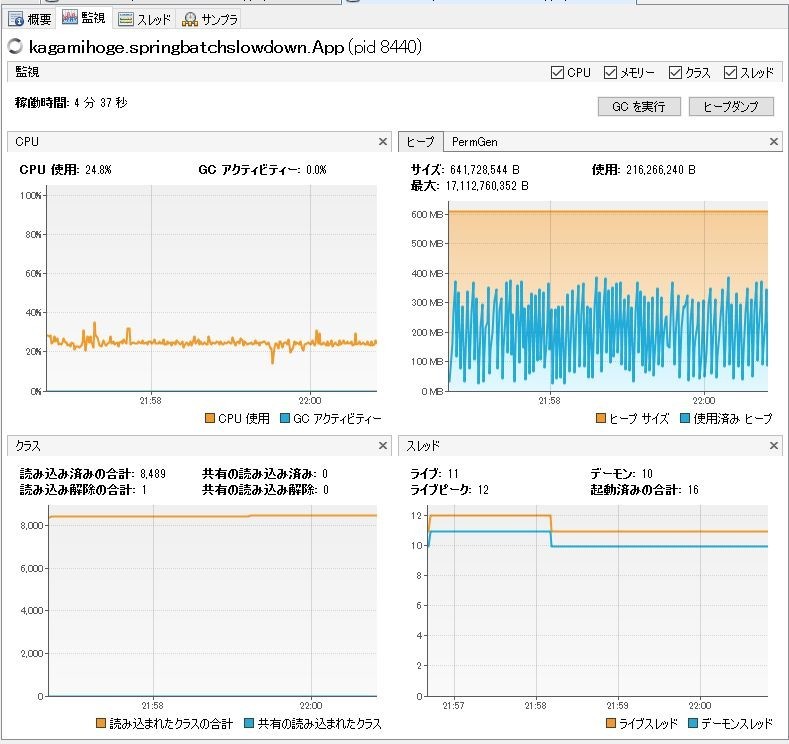
H2でやってみたがスローダウンはしなかった。もっと長時間起動し続けたらどうなるか分からんけど、そんなにもstep大量に実行するような状況とは最早別問題であろう。